We include products we think are useful for our readers. However, when you buy something through our retail links, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Sub-Types of Rosacea
What Type Do You Have?
Sub-Types of Rosacea, understanding the different skin conditions. It is devastating when you first find out you have Rosacea! Getting a better understanding about the sub-types of Rosacea, will help assist you manage it and its flare ups.
What is Rocacea?
Rosacea (rose-AY-shah) is a chronic, but treatable, skin condition that mostly affects the face, usually in the area where you blush. The symptoms of Rosacea can come and go in cycles which are often mistaken for acne or sunburn, and if left untreated, may get worse over time.
Rosacea may develop in many ways and at any age, but typically begins any time after age 30 as flushing or redness on the cheeks, nose, chin or forehead that may come and go. Studies have shown that over time the redness tends to become ruddier and more persistent, and visible blood vessels may appear.
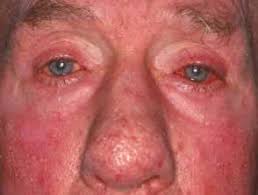
When left untreated, bumps and pimples start to develop, and in severe cases, particularly in men, the nose may grow swollen and bumpy from the skin thickening and forming excess tissue. About 50 percent of people with Rosacea will experience the their eyes being affected, feeling irritated and appearing watery or bloodshot. Symptoms vary by the different types of Rosacea and can range form mild to more severe within each sub-type.
Who Gets Rosacea?
People of all skin colors and skin types can get any of the types of Rosacea. It usually occurs in adults aged 30 and older. Often, those with Rosacea have parents or grandparents who have Rosacea or have had the same symptoms.
Women are more prone than men, but men tend to get it worse.
What Causes Rosacea?
Experts don’t exactly know what causes Rosacea, but it can be triggered, or aggravated, by a variety of factors. Each person’s triggers are different. If you have Rosacea, keeping track of your facial flare-ups may help you discover what those triggers are and help you to avoid them and future flare ups.
To identify your Rosacea triggers, keep a diary of daily activities and food intake for 2 weeks. Highlight the times that seem to coincide with a flushing or flare up episode. Then try to avoid them (if possible) to see it it reduces your flushing and flare ups.
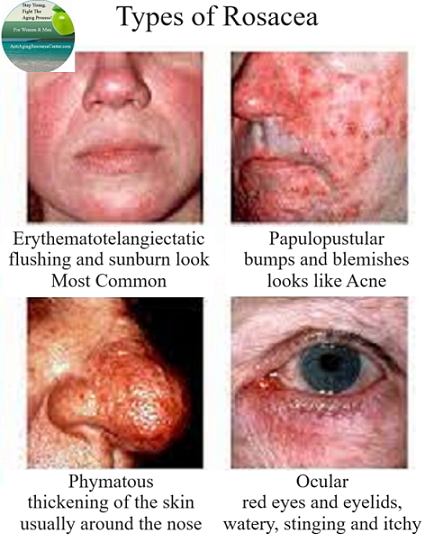
There Are Four Sub Types Of Rosacea
The sub types of rosacea are listed in order of severity.
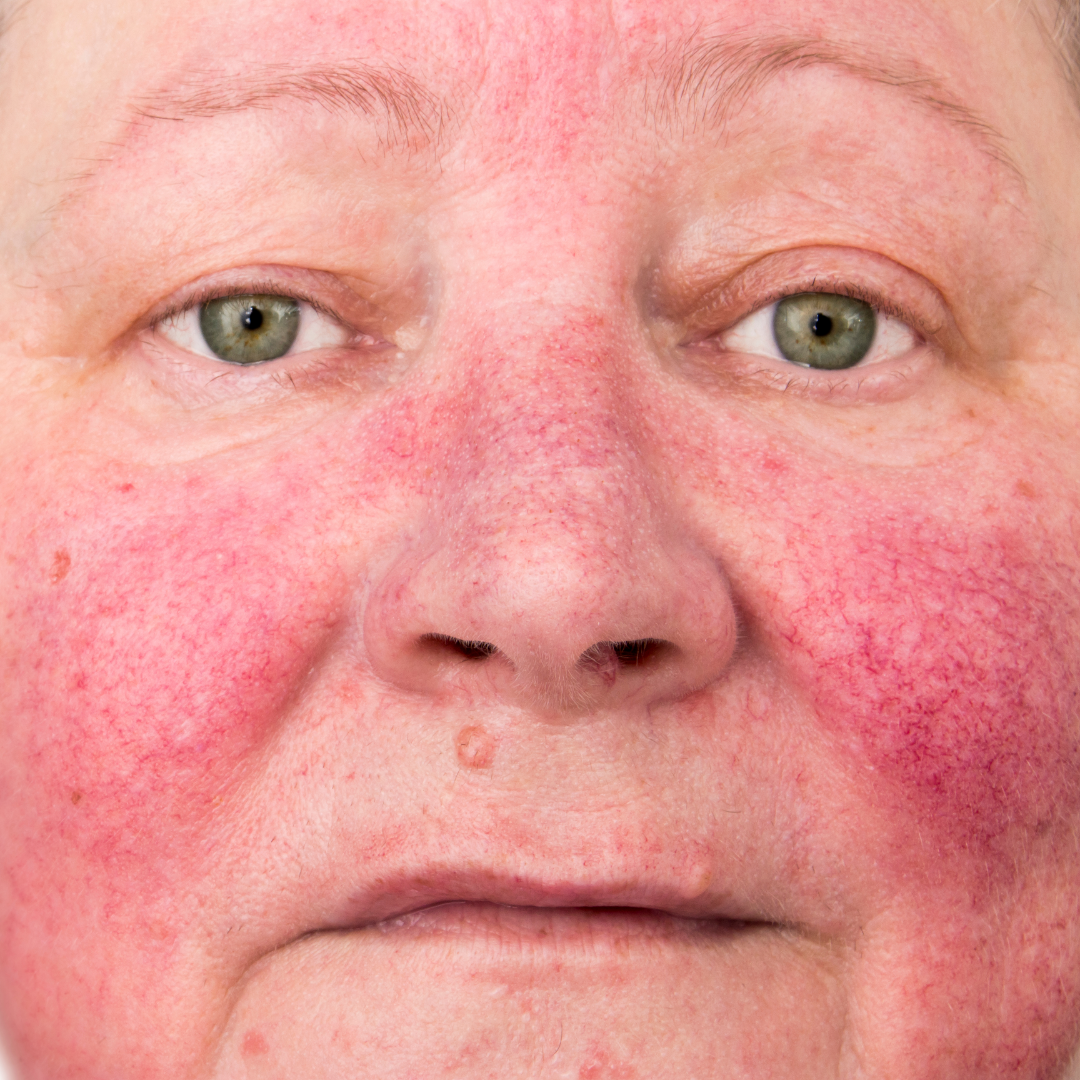
Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea
er-uh-THEE-muh-toh-tel-AN-jee-ek-TAT-ik
Not even the pronunciation helps!
We are going to call this Persistent Redness, and it is the most common sub-type of Rosacea.
It can look like blushing or sunburn. This happens when flushing causes small blood vessels under your skin to become enlarged, and this allows more blood to flow; leaving your skin looking red. Over time, this redness does not go a way!
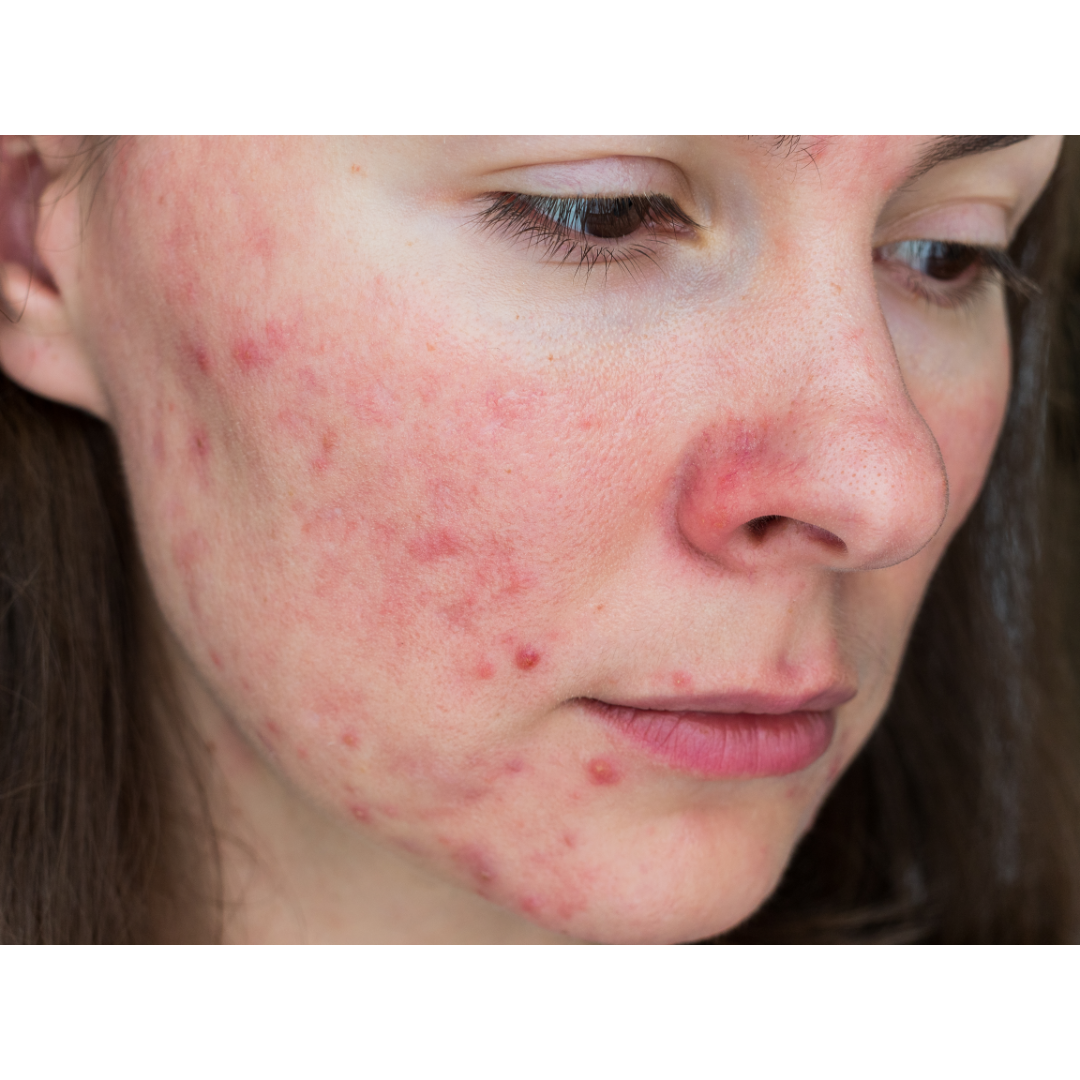
Papulopustular Rosacea
PAP-yew-lo-PUS-tyew-lar
This sub-type of Rosacea causes bumps and blemishes on your face that looks like acne and the most commonly treated type of Rosacea.
This is when constant inflammation can cause pimples, or papules (small, red, and solid) and pustules (pus filled, like some acne) to appear on your face.
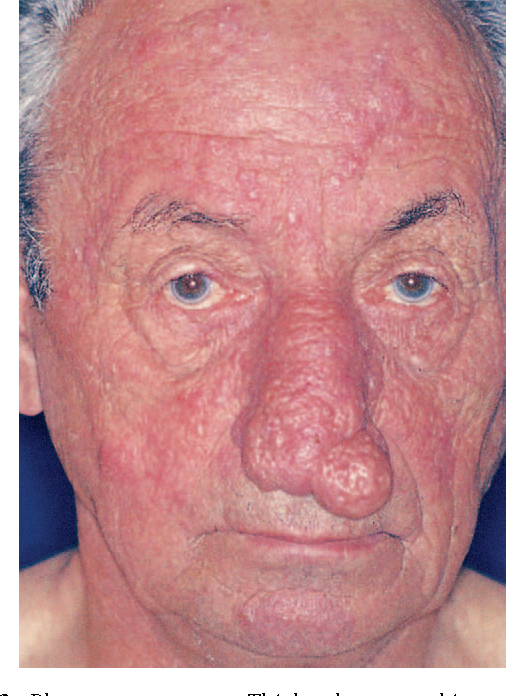
Phymatous Rosacea
(FY-muh-tus)
This the sub-type of Rosacea that thickens the skin. It usually appears around the nose and is more common in men.
Without early treatment, small knobby bumps can form making the nose look larger than normal and swollen.
Ocular Rosacea
OCK-yew-lar
This sub-type of Rosacea causes the eyes and eyelids to become red and bloodshot.
It also can cause burning or stinging, itching, dryness, light sensitivity, blurred vision or visible blood vessels.
How to Manage Your Rosacea
The New and Natural Way
The modern-day, new quicker way to treat Rosacea!
Acne Rosacea Treatment a combination of blue and red LED Light therapy is the modern-day effective & natural skincare treatment to help clear up acne rosacea. Using a LED system of blue and red light therapy, research shows they are more effective than conventional methods.
The conventional old slower way!
Only your doctor can tell if your symptoms are due to Rosacea and what type you have.The most commonly treated type of Rosacea is bumps and blemishes (papulopustular). There are prescription medications available that can be used to help manage this type of Rosacea. If you think you may have any type of Rosacea, seek professional help to find out, the earlier you find out the easier it is to manage it before it gets out of control!
Treatment typically starts with a topical medication and sometimes your doctor may prescribe an oral medication to help manage inflammation. You may see improvements in the first few weeks, although full results usually take up to 10 to 12 weeks.
Which Rosacea Treatment would you choose?
There are all natural treatments such as light therapy and natural topical solutions that can also be used to manage your Rosacea effectively. Most people get better and faster results with the use of light therapy, which is an all natural Rosacea skin treatment.
No prescription and no oral medications to worry about.
Rosacea
can be managed with on going natural light therapy treatments and avoiding your triggers.
Stopping treatment can result in flare-ups of your symptoms. Studies
have shown that many people who used some form of treatment and then stopped had
symptoms recur.
There is no cure for Rosacea, as of yet! Though staying on top of your treatment, you can make your syptoms go away and that smooth, clear beautiful skin.
Read More
Treating Acne Rosacea with a combination of blue and red LED therapy is the modern-day effective and natural skincare treatment to help clear up acne rosacea. Research shows these LED light systems are more effective than conventional methods for treating rosacea.
Symptoms of Candida Albicans and its fungal overgrowth have been found to be a common occurrence in many, systemic infections, illnesses, diseases and metabolic disorders including Rosacea.
National Rosacea Society offers members a Rosacea Diary booklet and other materials at no charge.The site has a great blog and tons of information.
Recent Articles
-
Guide To Botanical Facial Oils And Harnessing Their Anti-Aging Powers.
Feb 07, 24 06:48 PM
A complete guide to botanical facial oils that takes the guesswork out of these magical elixirs, and the powerful benefits that plant oils have to offer your skin. -
Is Exfoliating Your Skin Important? The answer is yes! Especially if..
Dec 29, 23 11:29 PM
Exfoliating your skin is important to help determine how radiant, healthy and younger looking our skin will feel and look so, exfoliating it is an important step in our skincare routine.. -
Healthy Water, What Is The Best Healthiest Drinking Water?
Dec 29, 23 01:11 PM
Healthy water keeps our cells regenerated, replenished and plump giving them the energy to rebuild and function properly. You want to give your body the best possible water available, right?